The Science Behind Chemical Peels: Chemical Peel Benefits and How They Transform Your Skin
- Jun 25, 2024
- 2 min read
Updated: Jul 12, 2024
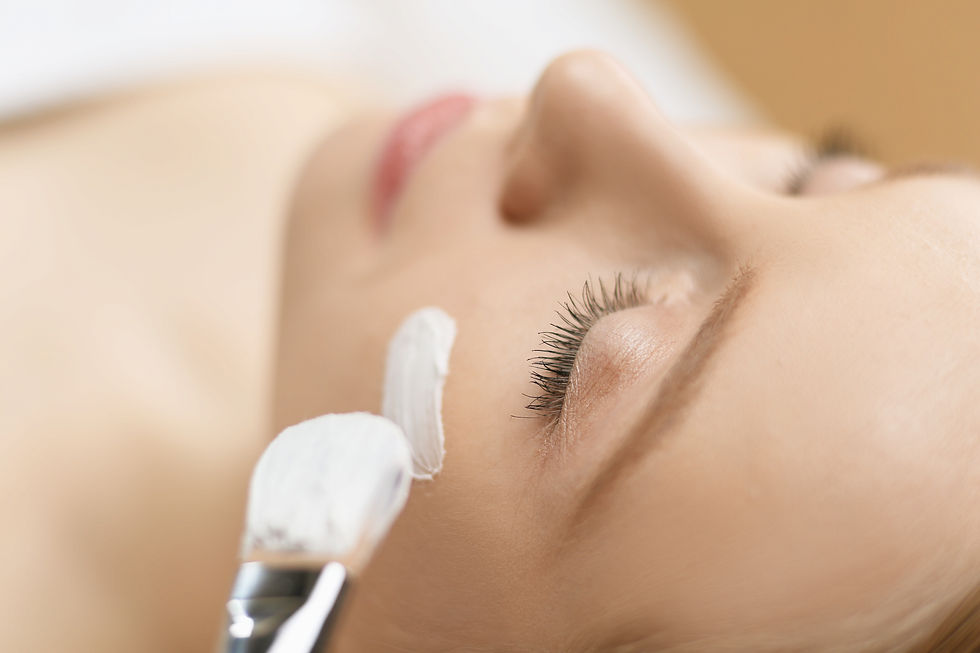
Chemical peels are popular skincare treatments that can improve the appearance of skin by removing dead cells and stimulating cell renewal. Understanding the science behind how chemical peels work can help you make an informed decision about incorporating them into your skincare routine.
Chemical peels work by applying a chemical solution to the skin, which causes it to exfoliate and eventually peel off. This process stimulates the growth of new skin cells, leading to smoother, more radiant skin.
There are three main types of chemical peels: superficial, medium, and deep. Superficial peels are the mildest and can improve the appearance of mild skin discoloration and rough skin. Medium peels penetrate the outer and middle layers of skin to remove damaged skin cells. Deep peels penetrate the deeper layers of skin to address more severe wrinkles and skin imperfections.
The benefits of chemical peels go beyond just improving the appearance of your skin. They can also help with acne, uneven skin tone, and sun damage. Additionally, chemical peels can stimulate collagen production, which can lead to firmer, more youthful-looking skin over time.
Exfoliation: Chemical peels contain acids such as alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs), beta hydroxy acids (BHAs), or trichloroacetic acid (TCA) that break down the bonds between dead skin cells, allowing them to be sloughed off.
Stimulation of Collagen Production: The exfoliation process triggers the skin's natural healing response, leading to increased collagen production. Collagen is essential for skin elasticity and firmness.
Reduction of Acne and Acne Scars: Chemical peels can help unclog pores, reduce inflammation, and fade acne scars over time.
Improvement of Skin Texture and Tone: By removing dead skin cells and stimulating cell turnover, chemical peels can result in smoother, more even-toned skin.
%20(1).png)




Comments